Learn
Savings Basics
There are five main college expenses.
Tuition, fees, housing, and food account for nearly 77% of the total cost of college.
What does one year of college cost today?
This quick snapshot gives you a good idea of what a year of college costs based on the type of school selected.
| In-State Undergrad On/Off Campus | Out-of-State Undergrad On/Off Campus | In-State Undergrad Living with Parents | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tuition/Fees* | $6,380 | $30,900 | $6,380 |
| Books, Course Materials, Supplies, Equipment | $1,235 | $1,235 | $1,235 |
| Transportation** | $1,660 | $1,660 | $1,660 |
| Living Expenses | $12,615 | $12,615 | $4,560 |
| Miscellaneous Personal Expenses | $2,234 | $2,234 | $2,234 |
| Federal Student Loan Fees | $56 | $56 | $56 |
| Total | $24,180 | $48,700 | $16,125 |
* Tuition/fee figures are projected estimates for 2025-26 for incoming freshmen entering UF for the first time (based on 30 credit hours total for the fall and spring semesters). Tuition/fees for continuing students may be lower.
**Transportation expenses are not qualified 529 plan expenses.
Source: University of Florida; Office of Student Financial Aid and Scholarships: 2025-2026
Most parents pay about 40% of the total cost of college for their child.
Families make up the difference with grants, scholarships, student loans, gifts from grandparents and other sources.
Source: Education Data Initiative: 2023 College Savings Statistics

There is power in starting early.
While it is never too late to save, there is a financial benefit in starting as soon as possible. When you start early, even small monthly contributions add up to big savings over time.
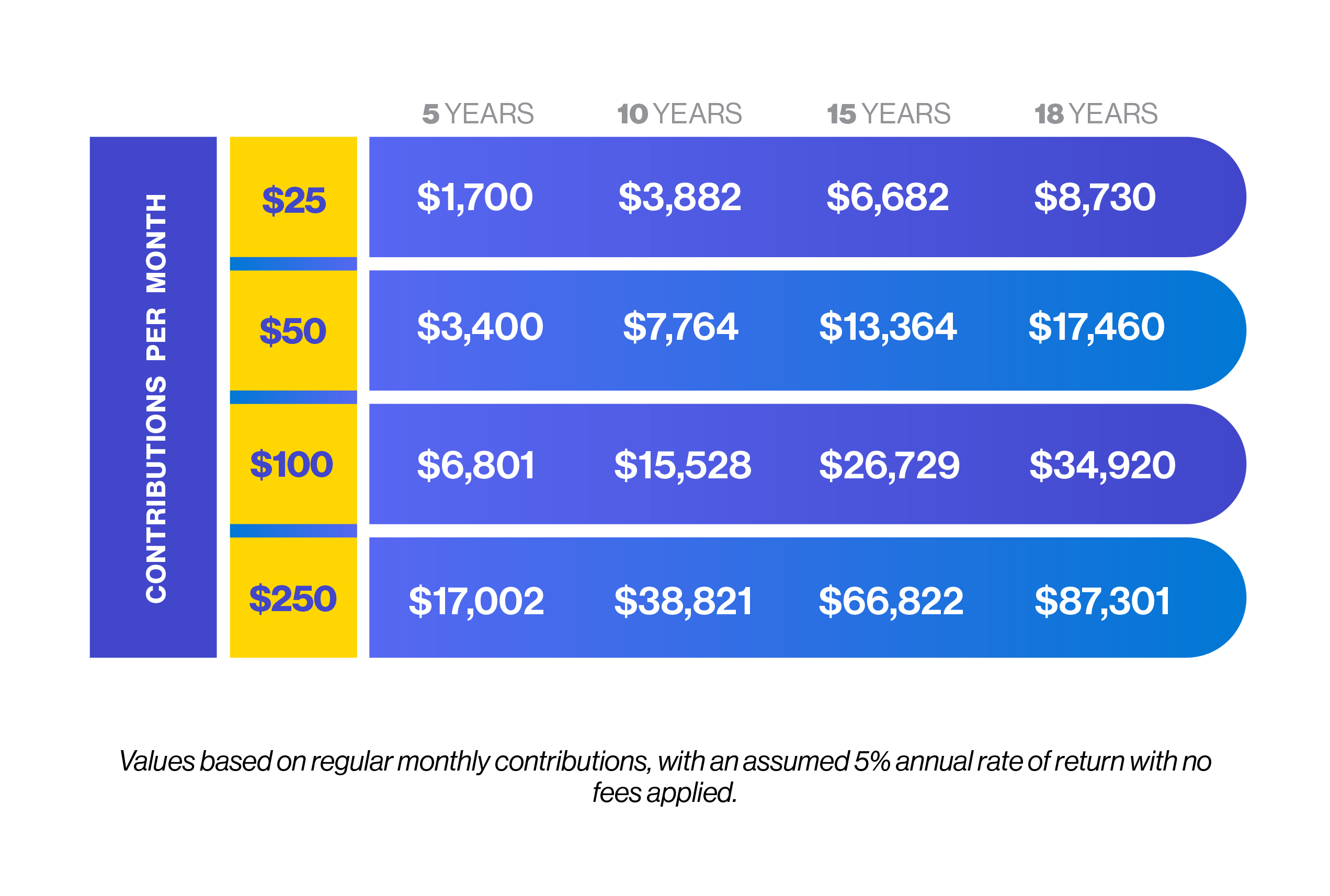
Save now or borrow later?
It is much better to have your interest work for you rather than against you. Over time, compounding interest can increase your savings, while repaying interest on a loan over time increases your debt.
Source: Florida Prepaid College Board
Savings Vocabulary 101
529 Plans
There are two types of 529 Plans – Prepaid and Investment. They are authorized by the IRS to encourage families to save for higher education while benefiting from tax-free growth.
Diversification/Diversify
An investment strategy that spreads funds among different plan types and/or asset classes.
Portfolio
A collection of financial assets, which could include a number of financial products like stocks, bonds, cash and cash equivalents, alternative investments, even life insurance, property or other assets.
Risk Tolerance
The level of risk an individual investor is willing to take when investing is referred to as their risk tolerance. Risk tolerance is based on individual financial goals and the speed at which an individual prefers to grow their investment account.
Asset Allocation
The combination of assets – stocks, bonds and money market funds – chosen for an investment portfolio is referred to as the total asset allocation.
Open Enrollment
A designated time period when plan pricing becomes available and one can enroll in and begin making payments on a Prepaid Tuition or Dormitory Plan.
Qualified Education Expenses
Qualified Higher Education Expenses (QHEE) include tuition and fees, housing and meal plans, books and supplies, as well as computers and equipment. Also, Investment 529 Plans may be used for K-12 tuition and other qualified expenses, up to $20,000 annually.
Rollover
A rollover involves the transfer of funds from one investment account to another (i.e., from one state’s 529 Plan to another, or an Investment 529 Plan to a student (beneficiary’s) Roth IRA (Individual Retirement Account)).
What is the best way to save for college?
Financial experts agree that 529 Plans are the smartest way to save for college because of the tax-free growth and flexibility.




Want to learn more?








